Blog > Post
Elasticsearch replaced Solr as the most popular search engine
by Paul Andlinger, 12 January 2016
Tags:
When we started to measure the popularity of search engines 3 years ago, Solr clearly dominated that category followed by Sphinx and Elasticsearch on the third rank. Since that time Elasticsearch impressively increased its popularity. It passed Sphinx in June 2013 and continuously reduced the gap to Solr, until it finally took the lead in our recent ranking.
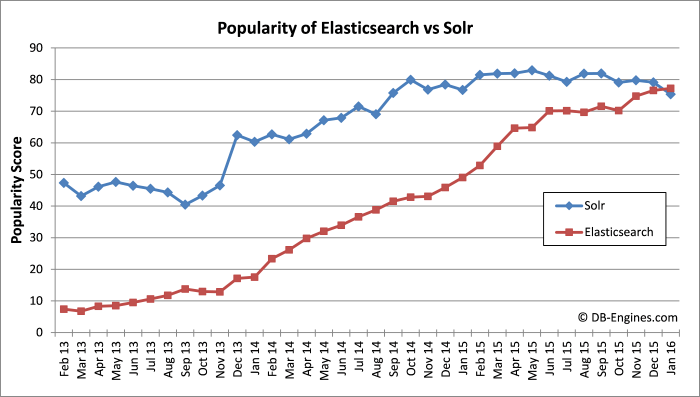
The DB-Engines popularity of a system is calculated by using several parameters like numbers of mentions on websites, number of technical discussions and relevance in social networks (description of methodology). But the parameter, which best reflects the trend of Elasticsearch is the number of job offerings with Elasticsearch skills required:
- in the past 3 years, Solr has almost doubled its job offerings; but the number of open jobs for Elasticsearch was exploding by a factor of 20 (!) during the same period. This is a strong indication that Elasticsearch is no longer only a Solr alternative for techies, but is used throughout the industry.
- Today we still count about 30% more open jobs for Solr than for Elasticsearch, but extrapolating from the current trend, it seems to be a matter of months that we will measure a reverse order here.
Elasticsearch and Solr are often considered as being mutually exchangeable twins, because they share many features:
- both are open source search engines,
- both are written in Java,
- both are based on the Apache Lucene Core libraries.
So, what could be the reason for Elasticsearch's latest success? As the answer can only be speculative, we nevertheless found some facts, which obviously have supported the trend:
- With the new major version 2.0 (released in autumn 2015), Elasticsearch brought several new features (a new type of aggregations, a simplified query language), improved performance and hardened security.
- Elastic, the commercial entity behind Elasticsearch rolled out two 'Elasticsearch-as-a-service' offerings. The first is aimed at developers and start-ups and allows a jump-start with Elasticsearch. The second one is a production grade offering, aimed at larger enterprises and includes additional support services.
- Elastic is heavily promoting its 'ELK stack', a fully-fledged analytics platform based on the open source tools Elasticsearch, Logstash (a data pipeline for processing and managing logs from various systems) and Kibana (a data visualization tool). The ELK stack faces competitors like Splunk or Datastax Enterprise (built on Cassandra, Solr and Apache Spark).
It will interesting to watch what the rivalry between Elasticsearch and Solr will bring in the future.
Share this page


 RSS Feed
RSS Feed



